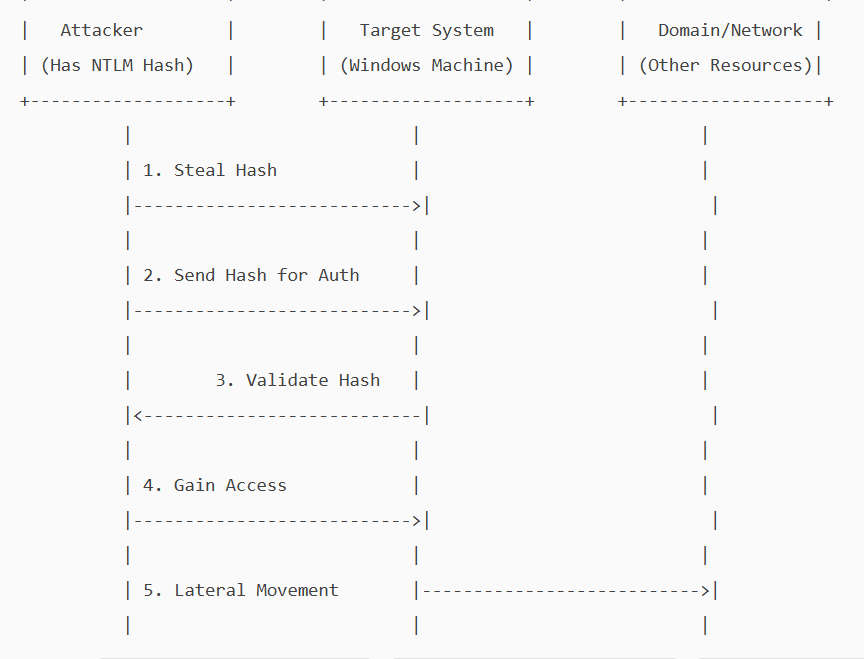
A pass-the-hash attack is a cybersecurity attack in which a malicious user steals hashed credentials from a compromised system and uses them to log in as the original user.
Hashing is an essential concept in cybersecurity and computer science. It involves using a mathematical algorithm, a hash function, to convert input data into a hash value. This process is deterministic and one-way, meaning it cannot be reversed to reveal the original data. i.e, It is not possible to get a clear-text password from a password hash.
On local systems, Windows stores passwords in a hashed, encrypted format in the Security Accounts Manager (SAM) database and caches them in LSASS(Local Security Authority Subsystem Service) memory during logon. If a malicious user obtains a password hash, they can execute a pass-the-hash attack.
NTLM (NT LAN Manager) is a Windows authentication protocol that uses a challenge-response mechanism. Instead of sending a password over the network, the client proves it knows the password by encrypting a server-issued challenge with the password’s hash (as a DES key)
The server verifies this response using its stored hash.
In a Pass-the-hash attack, the attacker exploits a vulnerability in the NTLM protocol to gain unauthorised access. The attacker does not need to know the clear-text password, as NTLM will accept the hash as proof of identity. He will pass the hash he obtained and will be allowed access as a legitimate user.
. Attackers can steal these hashes through various methods
- Memory dumping: They can extract hashes from the LSASS process’s memory using Mimikatz and Procdump.\
- Stealing SAM database: If an attacker has access to SAM, they could dump the hash from it.
- Malware – key loggers, rootkits can give them access to hashes.
- Active directory compromise.
- Packet sniffing.
NTLM is mainly kept for backward compatibility in Windows. Current versions of Windows primarily use Kerberos for domain authentication, but NTLM is still used where a system is not part of a domain.
Because of its vulnerability, Microsoft recommends disabling NTLM wherever possible.
Implementing a zero-trust architecture is the most effective way to prevent pass-the-hash attacks. Stick to the following to secure your Pc/network.
- Strong authentication and identity verification – implement MFA.
- Least privilege and Just-in-Time Access control.
- Continuous monitoring and anomaly detection
Leave a comment